

When fission chain reactions are desirable, even in controlled reactors, uranium is slightly enriched in the fissile isotope to ensure that there are enough fissile nuclei and free neutrons to maintain a chain reaction.

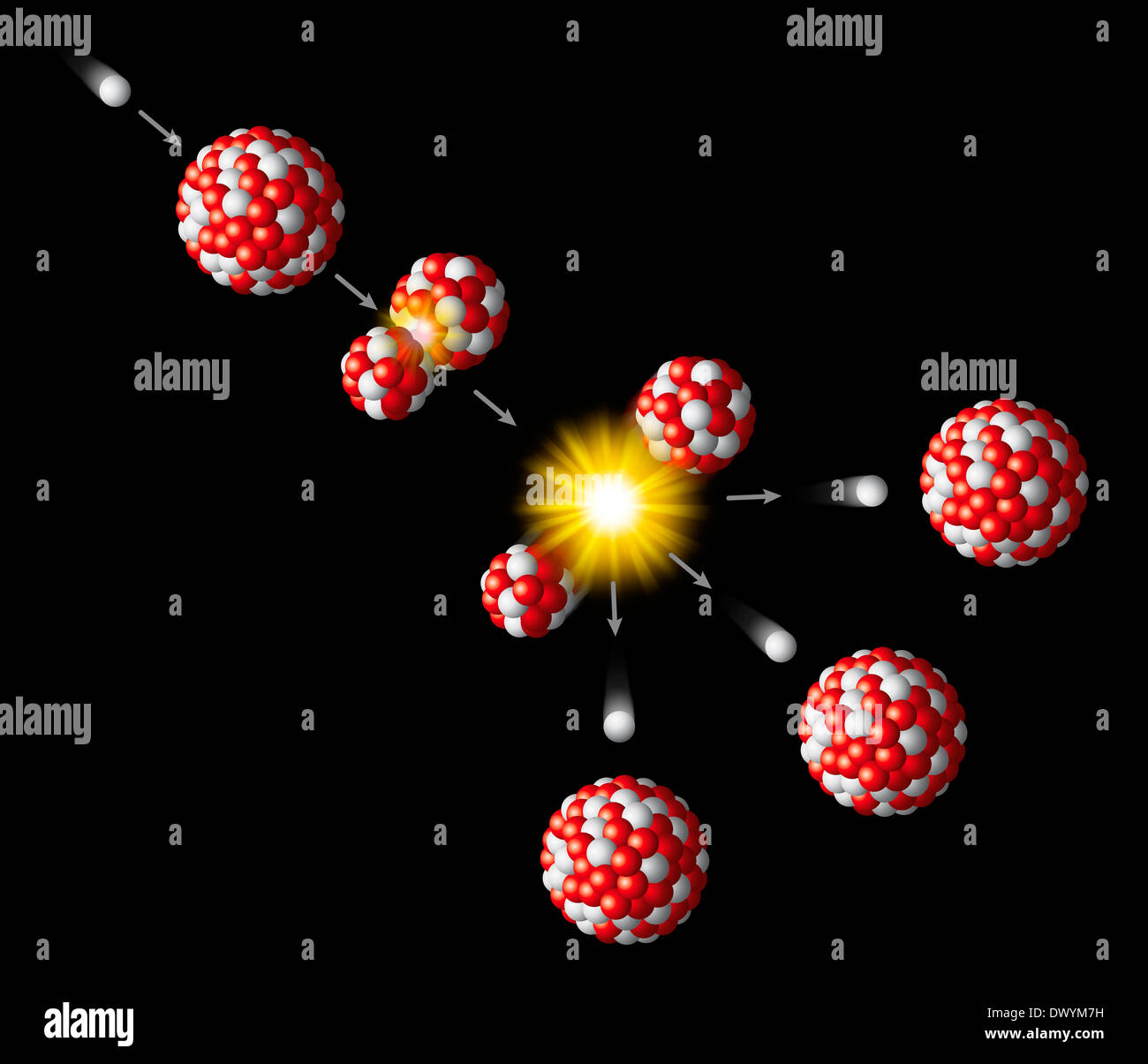
The free neutrons can go on to promote additional fissions in a chain reaction. Several neutrons accompany that process, since neither of the smaller resulting nuclei needed so many neutrons to find a home on the nuclear stability curve. However, when it comes to nuclear fission, uranium-235 can break into significantly large pieces, like the barium and krypton. The same is true of the most abundant isotope of uranium, uranium-238. Thorium by and large undergoes radioactive decay to become the smaller, stable nucleus of lead. The less-common uranium-235, with a half-life of about 700 million years, is one such nucleus. A fissile nucleus can be split into two or more smaller nuclei of substantial size, usually because of a collision with a neutron. A Fissile NucleusĬertain isotopes of these heavier actinoids are what scientists call ‘fissile’. But with uranium and elements to its right, there is a short-cut available, an alternative path to stability-the process of fission. The loss of two protons and two neutrons per alpha particle, successively, decreases the mass of the remaining nucleus on its way to a stable end point. Most radioactive isotopes, which are lighter than uranium, emit alpha particles as part of their decay chain. Only when enough fissile material is packed into a small enough volume can we reach the condition where neutron flux is sufficiently high to cause a runaway chain reaction. In both uranium and plutonium, a specific amount of weapons-grade material is necessary to achieve what is called ‘criticality’. (Image: adison pangchai/Shutterstock) The Decay Chain Plutonium-239 was used in the ‘Fat Man’ bomb dropped on Nagasaki-and a month earlier in a bomb test that took place in Alamogordo, New Mexico. Uranium-235 was used in the ‘Little Boy’ bomb dropped on Hiroshima. Davis Jr., Georgetown University The first and only nuclear devices ever deployed in wartime used extremely concentrated samples of fissile nuclei obtained through nuclear fission. Controlled fusion with release of energy has occurred, but no commercially viable method to generate electrical power has yet been constructed.By Ron B. It is used in thermonuclear weapons, where the fusion reaction proceeds unchecked. Because fusion requires extreme conditions, producing this nuclear reaction on Earth is a difficult technical problem.

The stars are ultimately the source of all the elements in the periodic table with Z greater than or equal to 6 (carbon). To fuse higher-Z nuclei together requires even more extreme conditions, such as those generated in novae and supernovae. Since the energy required to overcome the mutual electric repulsion of the two nuclei is enormous, fusion occurs only under extreme conditions, such as are found in the cores of stars and nuclear particle accelerators. More complicated fusion processes are possible these involve more massive nuclei. Four hydrogen nuclei (protons) combine in a multistep process to form a helium nucleus. Fusion of low-Z nuclei can release a considerable amount of energy. Fusionįusion occurs when two nuclei combine together to form a larger nucleus. In an atomic bomb, the chain reaction is explosively rapid. Nuclear reactors are designed so that the release of energy is slow and can be used for practical generation of energy. This process is carried on in a controlled manner in a nuclear reactor, where control rods capture excess neutrons, preventing them from being captured by other uranium nuclei to induce yet another uranium fission. When the uranium nucleus fissions, it releases a considerable amount of energy. This "chain reaction" process causes the number of uranium atoms that fission to increase exponentially. With a proper arrangement of uranium atoms, it is possible to have the neutrons resulting from the first fission event be captured and to cause more uranium nuclei to fission. Fission products will often emit neutrons because the N/Z ratio is greater at higher Z. For example, an excited state of uranium (created by neutron capture) can split into smaller " daughter" nuclei. Fission can occur spontaneously it may also be induced by the capture of a neutron. Fission occurs when the nucleus of an atom divides into two smaller nuclei.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
